Emulators
Emulation
- replication of internal processes of another hardware
- game console emulators - try to match or even improve the gameplay experience of the original HW
- Factors
- nostalgy
- quick but engaging gameplay (pick-up-and-play)
- emulation features (streaming, statistics, load/save, fast forward,...)
- the only way how to play certain games (Pokémon ROM hacks, fan-made translations)
- legal issues (downloading games you don't own a copy of is illegal)
History
- 1990 - Family Computer Emulator for NES
- 1993 - VICE emulator for Commodore 64
- 1995 - Virtual GameBoy
- 1997 - NESticle - emulator that defined retro-gaming
- 1997 - NO$GMB GameBoy emulator for DOS
- 1998 - PSEmu PlayStation emulator
- 2000 - VGBA GameBoy emulator
- 2001 - PSCX2 PS2 emulator
- 2002 - Dosbox, DOS full CPU emulator
- 2010 - RetroArch released, cross-platform front-end for emulators
- 2015 - revival of home-made arcade cabinets
- 2016 - Raspberry 3 released, a new wave of retro-gaming emerged
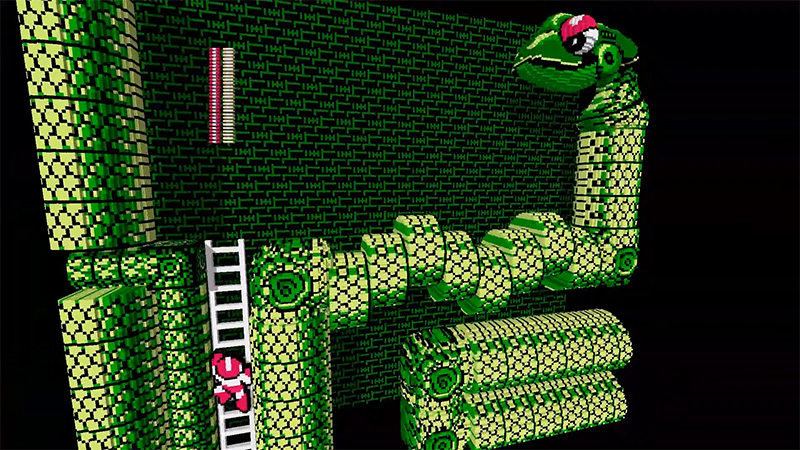
- 2020 - 3DSen beta version of 3D Voxel NES emulator
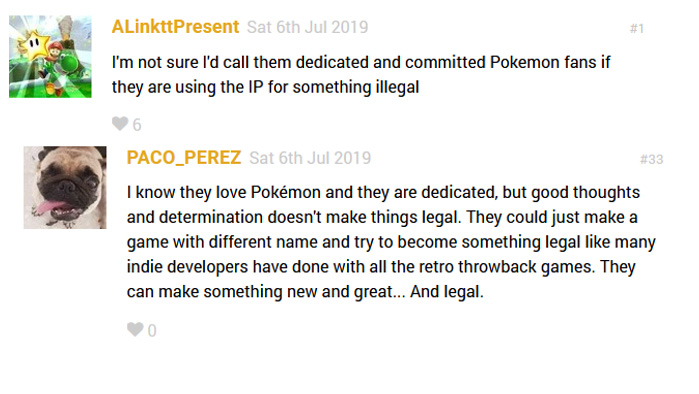
Pokémon ROM hacks
- fan-made mods of Pokémon games for GBC/GBA/3DS
- expansion into a universe the game has already established
- despite the fear of Nintendo, the community is still growing
- Pokémon Prism - full-fledged character customization, rewritten story
- Pokémon Light Platinum - rewritten story, based on Pokémon Ruby
- Pokémon Mega Power - new areas and story
- Pokémon Glazed - rewritten story
Raspberry
- full-fledged (not only) retro-gaming device
- Rpi 3 is capable of emulating C64, GBC, GBA, PSX, MegaDrive, NES, SNES, DOS (~486DX2 CPU)
- Rpi 4 is also more or less capable of emulating PSP, N64, and Dreamcast
- emulation is managed by libretro framework with RetroArch gui, running in Emulationstation front-end, powered by RetroPie OS