ThreeJS Introduction
ThreeJS
- HTML5 3D Animation Engine
- 3D JavaScript library
- WebGL-based
- Full scene graph, sprites, meshes, LOD, camera, shaders, animations
- Ideal for any 3D scene incorporated into a web page
Links
Architecture
Namespaces
- this is just a subset, there are over 600 classes

DisplayEntities
- EventDispatcher - parent of all displayable classes, implements event-based system
- Object3D - base class for 3D objects
- Audio - non-positional audio object
- Bone - bone which is part of a Skeleton
- Sprite - a plane that always faces towards the camera
- Camera - abstract class for all cameras
- CubeCamera - a group of 6 cameras that render to a WebGLCubeRenderTarget
- Group - adds ability to properly work with groups
- Points - 3D points in space
- SVGObject - class that displays SVG vector images
- LightHelper - displays a helper object for lights (e.g. cone for SpotLight)
- Light - abstract base class for lights
- Line - line segment
- LOD - wrapper for objects rendered with LOD technique
- Mesh - triangular polygon mesh-based objects
- Scene - a scene to which you can place objects, lights and cameras

Basic setup
import * as THREE from 'three';
let canvas = document.getElementById('gameCanvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
let camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, canvas.width / canvas.height, 0.1, 1000 );
let renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas });
renderer.setSize( canvas.width, canvas.height );
// add a cube
let geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry();
let material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( { color: 0xFF00FF } );
let cube = new THREE.Mesh( geometry, material );
let scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.add( cube );
camera.position.z = 5;
// game loop
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
WebGLRenderer parameters
export interface WebGLRendererParameters {
canvas?: HTMLCanvasElement | OffscreenCanvas; // canvas for rendering
context?: WebGLRenderingContext; // webgl rendering context
alpha?: boolean; // enables alpha channel
antialias?: boolean; // enable antialias
depth?: boolean; // enables depth buffer
stencil?: boolean; // enables stencil buffer
Camera attributes
fov: number, // field of view
aspect: number, // aspect ratio
near: number, // near plane
far: number // far plane
Update loop
- there is no ticker. You need to attach the animation loop to the event loop by calling
requestAnimationFrame() - you can use the
Clockobject to measure time
const clock = new THREE.Clock();
// start the clock
clock.start();
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
// get delta
const elapsedTime = clock.getDelta();
// ... update your model
// render your scene
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();
Loading
- There is a special loader for each asset type
AudioLoaderfor audioFileLoaderfor filesFontLoaderfor fontsImageLoaderfor imagesLoadingManagerfor event-based loadingMaterialLoaderfor materialsTextureLoaderfor textures
let textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
let texture = textureLoader.load('./assets/icon.png');
Positioning
- transformations are similar to PixiJS
positionrotation(Euler angles)quaternion(for global rotation)scale
Exercise
the exercise is relevant to a project version with a tag of 4.2
go to
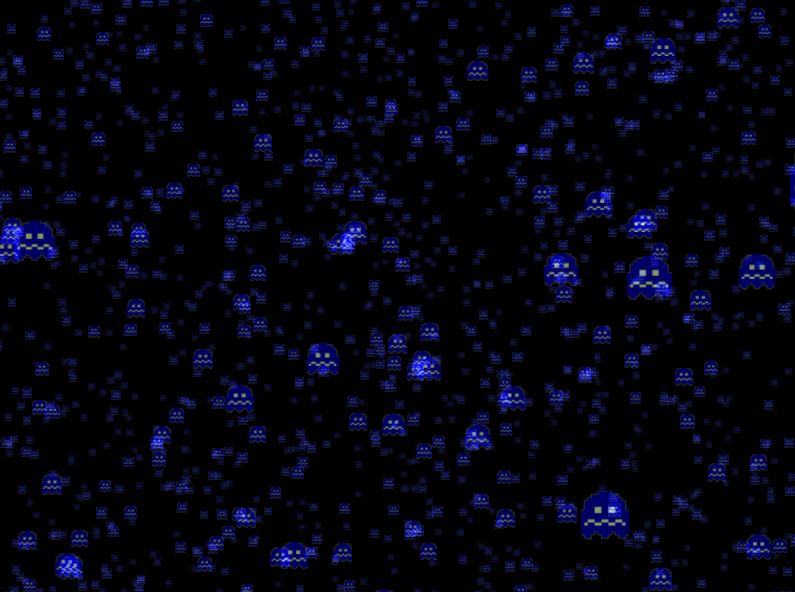
examples\src\02-three-intro\sprites.tsfollow the instructions in TODO blocks and render animated particles by the picture below
you can access the canvas in
http://localhost:1234/02_sprites.html